Load data from Microsoft Azure Storage
StarRocks allows you to load data in bulk from Microsoft Azure Storage by using Broker Load.
Broker Load runs in asynchronous mode. An asynchronous Broker Load process handles making the connection to Azure, pulling the data, and storing the data in StarRocks.
Broker Load supports the Parquet, ORC, and CSV file formats.
Advantages of Broker Load
- Broker Load runs in the background and clients do not need to stay connected for the job to continue.
- Broker Load is preferred for long-running jobs, with the default timeout spanning 4 hours.
- In addition to Parquet and ORC file formats, Broker Load supports CSV files.
Data flow
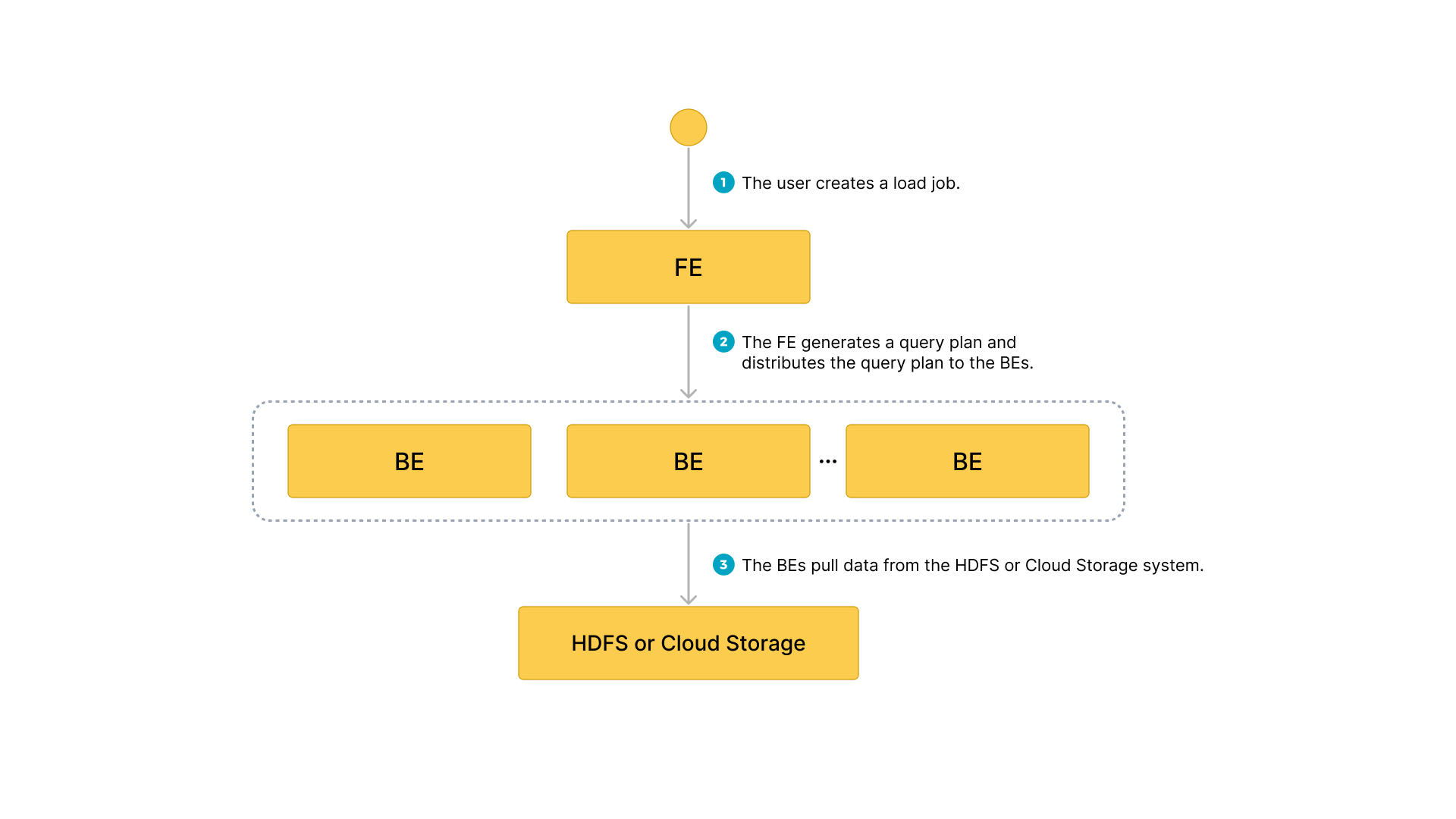
- The user creates a load job.
- The frontend (FE) creates a query plan and distributes the plan to the backend nodes (BEs) or compute nodes (CNs).
- The BEs or CNs pull the data from the source and load the data into StarRocks.
Before you begin
Make source data ready
Make sure that the source data you want to load into StarRocks is properly stored in a container within your Azure storage account.
In this topic, suppose you want to load the data of a Parquet-formatted sample dataset (user_behavior_ten_million_rows.parquet) stored in the root directory of a container (starrocks-container) within an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 (ADLS Gen2) storage account (starrocks).
Check privileges
You can load data into StarRocks tables only as a user who has the INSERT privilege on those StarRocks tables. If you do not have the INSERT privilege, follow the instructions provided in GRANT to grant the INSERT privilege to the user that you use to connect to your StarRocks cluster.
Gather authentication details
The examples in this topic use the Shared Key authentication method. To ensure that you have permission to read data from ADLS Gen2, we recommend that you read Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 > Shared Key (access key of storage account) to understand the authentication parameters that you need to configure.
In a nutshell, if you practice Shared Key authentication, you need to gather the following information:
- The username of your ADLS Gen2 storage account
- The shared key of your ADLS Gen2 storage account
For information about all the authentication methods available, see Authenticate to Azure cloud storage.
Typical example
Create a table, start a load process that pulls the sample dataset user_behavior_ten_million_rows.parquet from Azure, and verify the progress and success of the data loading.
Create a database and a table
Connect to your StarRocks cluster. Then, create a database and switch to it:
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS mydatabase;
USE mydatabase;
Create a table by hand (we recommend that the table have the same schema as the Parquet file you want to load from Azure):
CREATE TABLE user_behavior
(
UserID int(11),
ItemID int(11),
CategoryID int(11),
BehaviorType varchar(65533),
Timestamp varbinary
)
ENGINE = OLAP
DUPLICATE KEY(UserID)
DISTRIBUTED BY HASH(UserID);
Start a Broker Load
Run the following command to start a Broker Load job that loads data from the sample dataset user_behavior_ten_million_rows.parquet to the user_behavior table:
LOAD LABEL user_behavior
(
DATA INFILE("abfss://starrocks-container@starrocks.dfs.core.windows.net/user_behavior_ten_million_rows.parquet")
INTO TABLE user_behavior
FORMAT AS "parquet"
)
WITH BROKER
(
"azure.adls2.storage_account" = "starrocks",
"azure.adls2.shared_key" = "xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
)
PROPERTIES
(
"timeout" = "3600"
);
This job has four main sections:
LABEL: A string used when querying the state of the load job.LOADdeclaration: The source URI, source data format, and destination table name.BROKER: The connection details for the source.PROPERTIES: The timeout value and any other properties to apply to the load job.
For detailed syntax and parameter descriptions, see BROKER LOAD.
Check load progress
You can query the progress of Broker Load jobs from the loads view in the StarRocks Information Schema. This feature is supported from v3.1 onwards.
SELECT * FROM information_schema.loads \G
If you have submitted multiple load jobs, you can filter on the LABEL associated with the job:
SELECT * FROM information_schema.loads WHERE LABEL = 'user_behavior' \G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
JOB_ID: 10250
LABEL: user_behavior
DATABASE_NAME: mydatabase
STATE: FINISHED
PROGRESS: ETL:100%; LOAD:100%
TYPE: BROKER
PRIORITY: NORMAL
SCAN_ROWS: 10000000
FILTERED_ROWS: 0
UNSELECTED_ROWS: 0
SINK_ROWS: 10000000
ETL_INFO:
TASK_INFO: resource:N/A; timeout(s):3600; max_filter_ratio:0.0
CREATE_TIME: 2023-12-28 16:15:19
ETL_START_TIME: 2023-12-28 16:15:25
ETL_FINISH_TIME: 2023-12-28 16:15:25
LOAD_START_TIME: 2023-12-28 16:15:25
LOAD_FINISH_TIME: 2023-12-28 16:16:31
JOB_DETAILS: {"All backends":{"6a8ef4c0-1009-48c9-8d18-c4061d2255bf":[10121]},"FileNumber":1,"FileSize":132251298,"InternalTableLoadBytes":311710786,"InternalTableLoadRows":10000000,"ScanBytes":132251298,"ScanRows":10000000,"TaskNumber":1,"Unfinished backends":{"6a8ef4c0-1009-48c9-8d18-c4061d2255bf":[]}}
ERROR_MSG: NULL
TRACKING_URL: NULL
TRACKING_SQL: NULL
REJECTED_RECORD_PATH: NULL
For information about the fields provided in the loads view, see see Information Schema.
After you confirm that the load job has finished, you can check a subset of the destination table to see if the data has been successfully loaded. Example:
SELECT * from user_behavior LIMIT 3;
If data can be successfully returned, the data loading succeeds.
The system returns a query result similar to the following, indicating that the data has been successfully loaded:
+--------+---------+------------+--------------+---------------------+
| UserID | ItemID | CategoryID | BehaviorType | Timestamp |
+--------+---------+------------+--------------+---------------------+
| 142 | 2869980 | 2939262 | pv | 2017-11-25 03:43:22 |
| 142 | 2522236 | 1669167 | pv | 2017-11-25 15:14:12 |
| 142 | 3031639 | 3607361 | pv | 2017-11-25 15:19:25 |
+--------+---------+------------+--------------+---------------------+
